Understanding Battery Capacity Buffer and Tolerance in Tesla
- rory lee
- Aug 13, 2025
- 3 min read
When it comes to Tesla's electric vehicle (EV) batteries, many owners may notice that the actual usable battery capacity doesn’t always align perfectly with the manufacturer’s specified value. This discrepancy is primarily due to the capacity buffer and tolerance that Tesla builds into its battery packs to ensure the longevity and safety of the battery.
What is a Capacity Buffer?
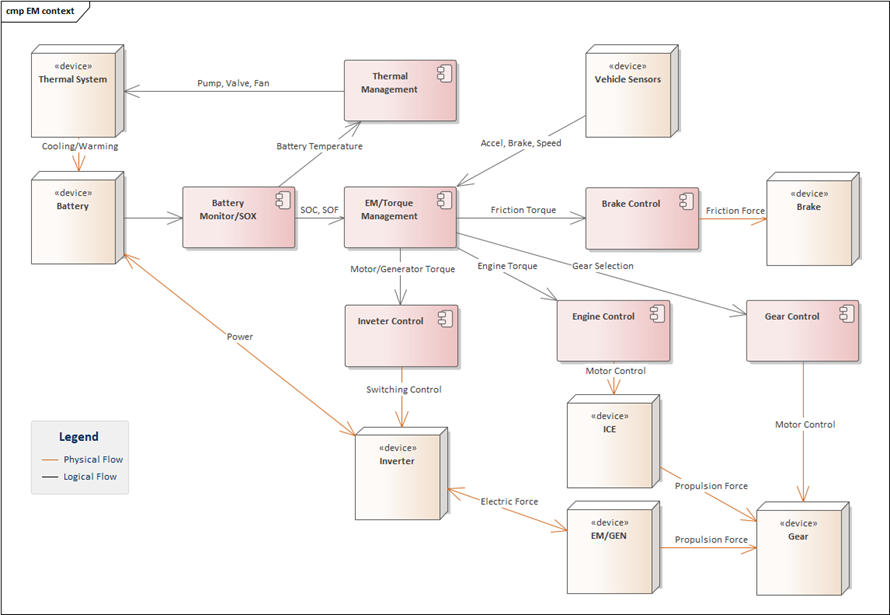
A capacity buffer is a portion of the battery’s total capacity that is intentionally reserved to account for errors in estimating the usable energy and to prevent overestimation of the remaining power capacity. This buffer ensures that the battery management system doesn't falsely report the battery as having more energy than it can actually deliver, protecting the system from inaccuracies during operation.
This buffer is essential for the State of Charge (SOC), State of Health (SOH), and State of Power (SOP) estimations that are used in modern EV battery management systems.
Source: J. Lee and L. Wang, "A method for designing and analyzing automotive software architecture: A case study for an autonomous electric vehicle," 2021 International Conference on Computer Engineering and Artificial Intelligence (ICCEAI), Shanghai, China, 2021, pp. 20-26, doi: 10.1109/ICCEAI52939.2021.00004.
These technologies allow the vehicle to accurately measure and monitor the battery's condition, providing real-time data on how much energy is actually available, how much capacity has been degraded, and how much power the battery can supply without compromising safety.
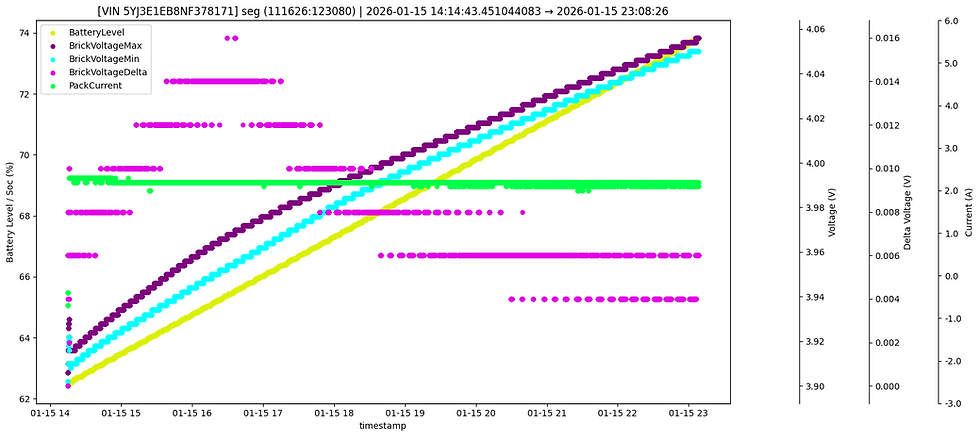
While the real capacity (e.g., 80 kWh) represents the total amount of energy the battery can store, the nominal capacity (or specification capacity) is typically lower, reflecting the energy capacity that the manufacturer advertises, excluding any error buffer. For example, a Tesla with a real capacity of 80 kWh might have a nominal capacity of around 77 kWh, as specified by the manufacturer. The usable capacity is typically lower than the nominal capacity because it can vary depending on factors such as driving behavior, weather conditions, and battery management strategies. Specifically, high-performance vehicles that require higher C-rates for charging and discharging can further reduce the usable capacity, as more energy is drawn during high power demands. The SOC, SOH, and SOP systems require an error buffer to account for potential errors in estimating the usable energy and remaining power capacity. Without this buffer, these systems could overestimate the available energy or the remaining capacity, leading to potential risks.
Battery Tolerance and Variations Between Packs
Even in identical Tesla models, slight differences in battery capacity can occur due to manufacturing tolerances. Tesla's batteries are made up of thousands of individual cells, and while they are designed to be as uniform as possible, small variations in their chemistry and performance can lead to slight differences between individual battery packs.
These natural variations in manufacturing tolerance can cause small differences in the actual usable capacity of each pack. While these differences are typically minor, they explain why two Teslas of the same model may show slight variations in their real battery capacity.
Tesla’s Low Capacity Buffer and Its Impact on Efficiency
Tesla is known for its relatively low capacity buffer compared to other manufacturers. By using a smaller portion of the battery’s capacity for the buffer, Tesla allows users to access more of the battery’s actual usable capacity, which helps improve the overall efficiency of the vehicle.
The smaller buffer also means that the vehicle carries less weight. Since batteries are one of the heaviest components of an EV, minimizing the buffer reduces the overall weight of the car. A lighter vehicle consumes less energy, which translates to improved driving efficiency and longer driving range on a single charge.

Source (https://ev-database.org/)
Tesla’s approach to having a low buffer enables the company to achieve a balance between battery longevity and performance. The vehicle can use more of the available energy without sacrificing the overall lifespan of the battery.

Comments