Case Study: Analysis of Cell Voltage Deviations in Tesla Model Y LFP Battery Charging
- rory lee
- Jun 14, 2025
- 2 min read
Updated: Jul 7, 2025
The analysis presented above is an actual case demonstrating the advanced battery diagnostics and management recommendations provided by Dr.EV. When critical battery alerts, such as cell voltage imbalances or unusual charging behavior, are detected through the Dr.EV app, our experts conduct in-depth investigations to pinpoint the root causes and provide personalized guidance.
In this case, we analyzed precise charging cycle data, identified notable voltage deviations during trickle charging, assessed battery health (SOH), and provided actionable advice on cell balancing strategies.
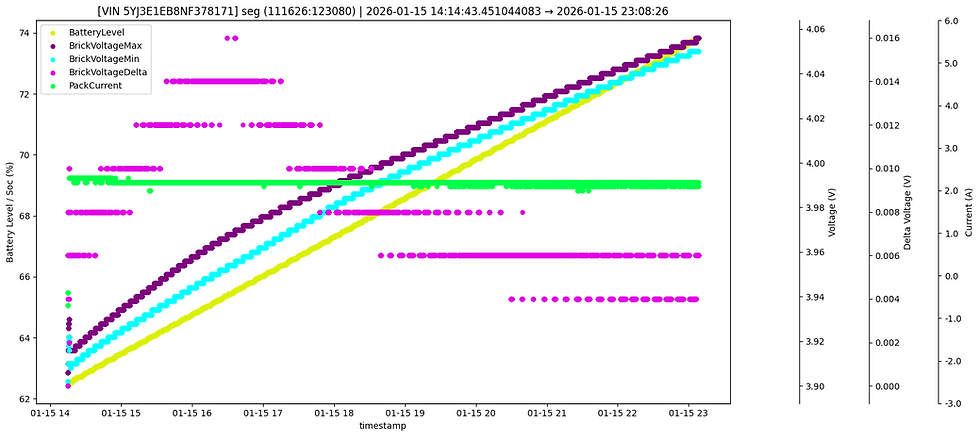
Upon analyzing the complete charging cycle data for the subject vehicle, it was consistently observed that the minimum cell voltage (blue) and maximum cell voltage (black) significantly diverged near the full-charge completion point. In contrast, voltage deviations during partial charges were minimal.

For more precise investigation, further analysis specifically focused on the battery level around 99%, the point where trickle charging occurs.

During trickle charging, the battery level remains steady at 99% while charging continues, resulting in a progressive increase in the gap between minimum and maximum cell voltages, reaching up to approximately 0.3V.

Additional comparisons were conducted on two other vehicles under identical full-charge conditions, revealing that these vehicles maintained much smaller cell voltage deviations (approximately 0.1V), significantly lower than the analyzed vehicle.


Analysis Conclusion:
Tesla’s BMS typically holds the battery level steady at 99% during the final trickle-charging phase, then jumps to a 100% reading upon actual completion. The notable voltage deviations between individual cells at this stage could arise due to:
1. Incomplete or insufficient cell balancing causing voltage imbalance among cells.
2. Presence of certain cells with relatively superior performance causing noticeable voltage gaps. (Note: Scenario #2 is actually indicative of higher-quality cells and is a positive sign.)
Considering that the battery's State of Health (SOH) for this vehicle remains within a normal range, the observed voltage deviations are likely within Tesla’s designed and acceptable operational parameters. Nonetheless, continuous observation and careful management are recommended due to the relatively larger deviations compared to other vehicles.
Recommended Actions:
Based on this analysis, the following recommendations are provided:
1. Perform Tesla’s official battery health test to facilitate algorithm calibration.
2. Utilize the Dr.EV App’s cell balancing mode, periodically employing a slow charger whenever you have available time (balancing may take up to approximately 60 hours).
3. Preferentially use slow chargers for the foreseeable future to encourage natural cell balancing.
4. Regularly monitor both battery SOH and inter-cell voltage deviations.
In summary, the observed inter-cell voltage deviation occurs specifically within the trickle-charging phase and does not pose any immediate concern to battery performance or safety. It falls within Tesla’s normal management parameters. However, due to the comparatively large deviations observed, ongoing monitoring and proactive management are advisable.

Comments